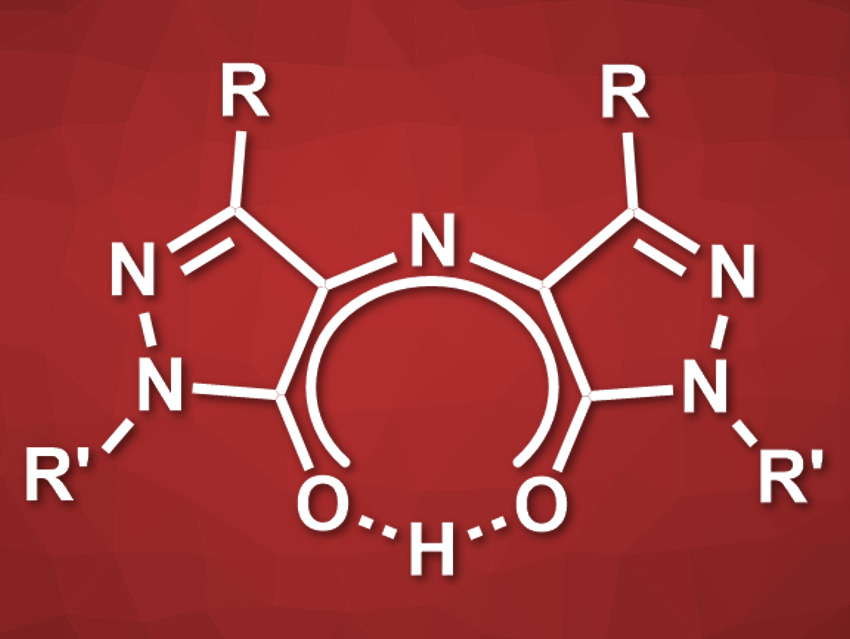
Rubazonic acid (pictured, R = Me, R’ = Ph) is a red dye that has been known since 1887. This compound and its derivatives could be useful as functional dyes, e.g., for sensors or materials. However, rubazonic acids have not been well studied and there is a lack of methods for their synthesis.
Stefan F. Kirsch, University of Wuppertal, Germany, and colleagues have developed a one-pot procedure for the synthesis of rubazonic acid derivatives. The team started from pyrazolones, which were diazidated by reacting them with sodium azide in the presence of iodine in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) at room temperature. The diazidated products were then converted to the desired dyes by dimerization, using a saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution as a reducing agent.
The team synthesized rubazonic acid derivatives with a range of different substituents in moderate to good yields. For the more challenging substrates, they developed an alternative two-step approach. In this method, the diazido intermediates were reduced with hydrogen over a Pd/C catalyst to give the corresponding rubazonic acids in improved yields.
- Rubazonic Acids and Their Synthesis,
My Linh Tong, Lena Theresa Leusch, Kristina Holzschneider, Stefan F. Kirsch,
J. Org. Chem. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.0c00465