Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are a growing problem in healthcare. Antibiotic compounds and materials with new modes of action are, thus, urgently needed. Nanomaterials with antimicrobial properties, for example, are promising for this type of application.
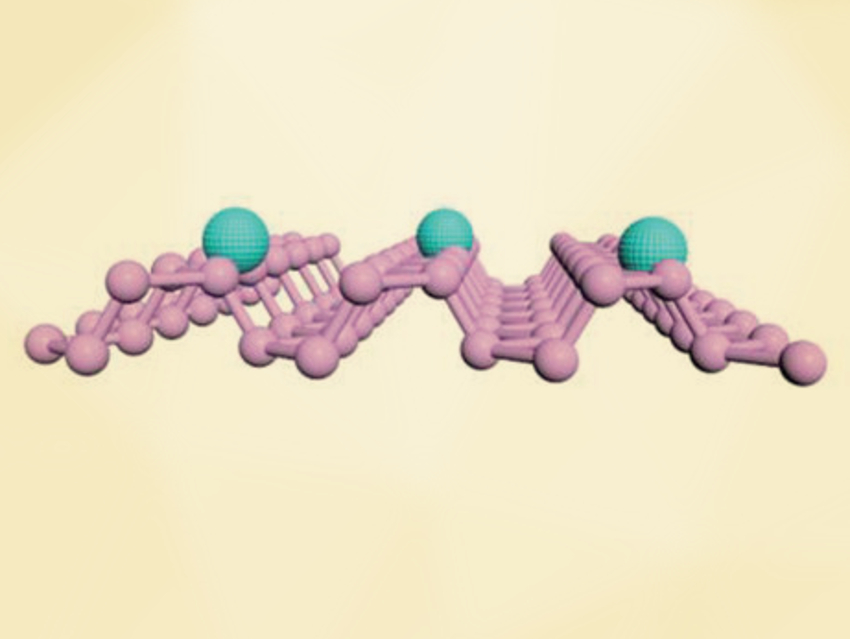
Chunsen Li, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Fuzhou, Fuan Wang, Wuhan University, China, and colleagues have developed such an antimicrobial material: silver-nanoparticle (AgNP)–doped black phosphorus nanosheets (BPNs, pictured). The team first prepared BPNs from bulk black phosphorus by ultrasonic exfoliation. The AgNPs on the nanosheets were then created by adding AgNO3 to a BPNs solution. The BPNs reduce Ag+ without a need for additional reducing agents.
According to the team, the resulting nanocomposite combines the known good antibacterial properties of AgNPs with the added stability and additional antimicrobial effect provided by the BPNs. The composite shows better properties than its separate components. The team found that the bacterial disinfection of the material is enhanced under sunlight. This is attributed to photogenerated reactive oxygen species (ROS). The AgNPs provide a preferred site for the adsorption and activation of O2, while BPN acts as a photocatalyst. Simultaneously, the AgNPs lead to a significantly increased affinity of the material toward bacteria, which promotes their inactivation. According to the team, the nanohybrids provide a cost‐effective and biocompatible antibacterial platform.
- Silver‐Laden Black Phosphorus Nanosheets for an Efficient In Vivo Antimicrobial Application,
Meijuan Liang, Minyi Zhang, Shanshan Yu, Qiong Wu, Kang Ma, Yingying Chen, Xiaoqing Liu, Chunsen Li, Fuan Wang,
Small 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201905938