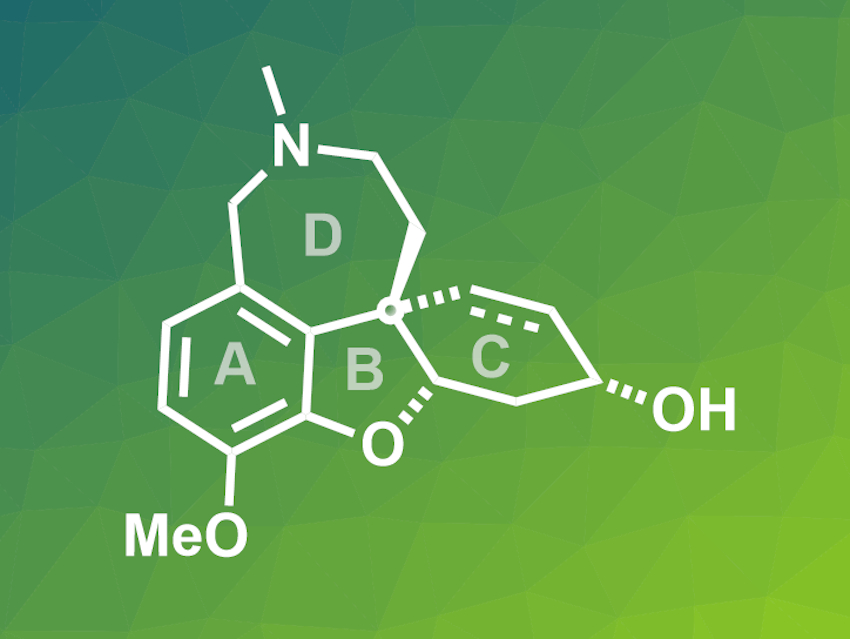
The alkaloid (–)-galanthamine, produced by snowdrop flowers, is as an inhibitor of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. Due to this effect, it can be used to treat Alzheimer’s disease and has been approved as a drug. Since it is a pharmacologically active molecule with an interesting chemical structure, galanthamine has been the target of different total synthesis approaches.
Fu-Min Zhang, Lanzhou University, Yong-Qiang Tu, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China and colleagues have performed total syntheses of (–)-galanthamine and the structurally related (–)-lycoramine (general structure pictured, dashed bond only in galanthamine). The syntheses proceed via a direct, catalytic, and enantioselective assembly of the cis-hydrodibenzofuran core of the molecule (rings A, B, and C). This structure was prepared by a six-step route starting from commercially available 3-butyn-1-ol, using a Pd-catalyzed Suzuki coupling and a spirocyclic pyrrolidine (SPD)-catalyzed enantioselective Robinson annulation reaction. This core was functionalized by a series of oxidation and reduction reactions and the product was converted to galanthamine using a Pictet-Spengler cyclization for the final ring-closing step. If the double bond in the ABC intermediate is reduced first, an analogous reaction sequence gives lycoramine.
The work shows that the spirocyclic pyrrolidine (SPD)-catalyzed enantioselective Robinson annulation, previously used for the synthesis of morphine and codeine, has the potential to allow easier access to a variety of natural products. According to the researchers, the method also provides an alternative path to galanthamine-type alkaloids and their analogues, which could be used for syntheses of lead compounds for pharmaceutical screening.
- Catalytic Asymmetric Total Syntheses of (−)-Galanthamine and (−)-Lycoramine,
Qing Zhang, Fu-Min Zhang, Chang-Sheng Zhang, Si-Zhan Liu, Jin-Miao Tian, Shao-Hua Wang, Xiao-Ming Zhang, Yong-Qiang Tu,
J. Org. Chem. 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.9b01971