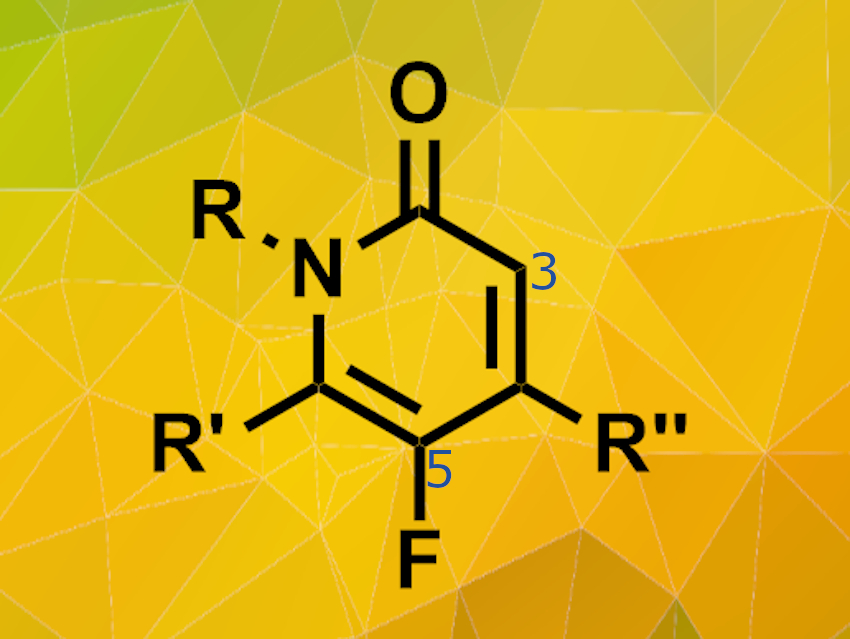
Regioselective fluorination is an important step during the synthesis of various bioactive organic molecules. Fluorinated molecules often display increased biological activity and improvements in pharmacokinetics such as higher metabolic stability. However, elemental fluorine and many fluorination agents are highly reactive and, thus, often yield product mixtures.
Fumie Sakurai, Drug Discovery Chemistry Laboratories, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Fujisawa, Japan, and colleagues have developed a direct fluorination process for N-protected pyridone derivatives. This process selectively introduces the fluorine atom at the 5-position of the pyridone structure.The team used N-fluorobenzenesulfonimide (NFSI) as fluorinating agent, various pyridone substrates and acetonitrile as the solvent. The reactions were carried out at 60°C.
The fluorination reaction is highly selective and works on a wide scope of substrates including mono- and bicyclic pyridones. Electron-donating groups as well as electron-withdrawing groups in 3-position are tolerated. However, strong electron-withdrawing groups like –CF3 require longer reaction times and higher reaction temperatures. The desired fluorinated products are obtained in medium yields at relatively mild conditions.This process makes new potential fluorinated drug candidates accessible because pyridone derivatives can now be fluorinated regioselectively at a late stage of the synthesis process.
- Direct and Regioselective Monofluorination of N-Protected Pyridone Derivatives using N-Fluorobenzenesulfonimide (NFSI),
Fumie Sakurai, Takafumi Yukawa, Takahiko Taniguchi,
Org. Lett. 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.9b02482