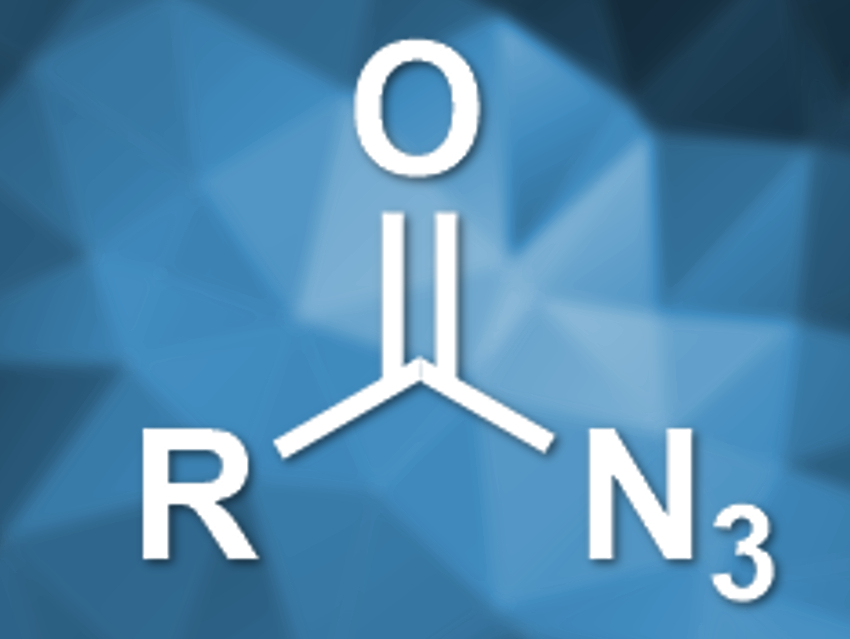
Palladium-catalyzed carbonylations of azides using CO can be used to prepare isocyanates. Acyl azides, however, are very reactive and can undergo unwanted rearrangement reactions. Thus, they had not been used in this type of reaction so far. Acyl ureas are a possible product of this reaction pathway. They are usually prepared either with stiochiometric byproducts or by using the toxic phosgene, both of which are problematic.
Zhenhua Zhang, China Agricultural University, Beijing, and colleagues have developed a palladium-catalyzed carbonylation of acyl azides with CO, which can be used to prepare acyl ureas. The team used Pd(OAc)2 as a catalyst, 1,10-phenanthroline as a ligand, and tetrahydrofuran (THF) as the solvent to convert acyl azides, CO, and amines to acyl ureas (pictured below).
.jpg)
The desired products were obtained in good to excellent yields. The reaction proceeds at room temperature and has a broad substrate scope. The proposed reaction mechanism involves an unusual five-membered palladacycle intermediate. According to the researchers, other Pd-catalyzed reactions of azides with a similar mechanism could be possible.
- Pd-Catalyzed Carbonylation of Acyl Azides,
Zongyang Li, Shiyang Xu, Baoliang Huang, Chenhui Yuan, Wenxu Chang, Bin Fu, Lei Jiao, Peng Wang, Zhenhua Zhang,
J. Org. Chem. 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.9b01048