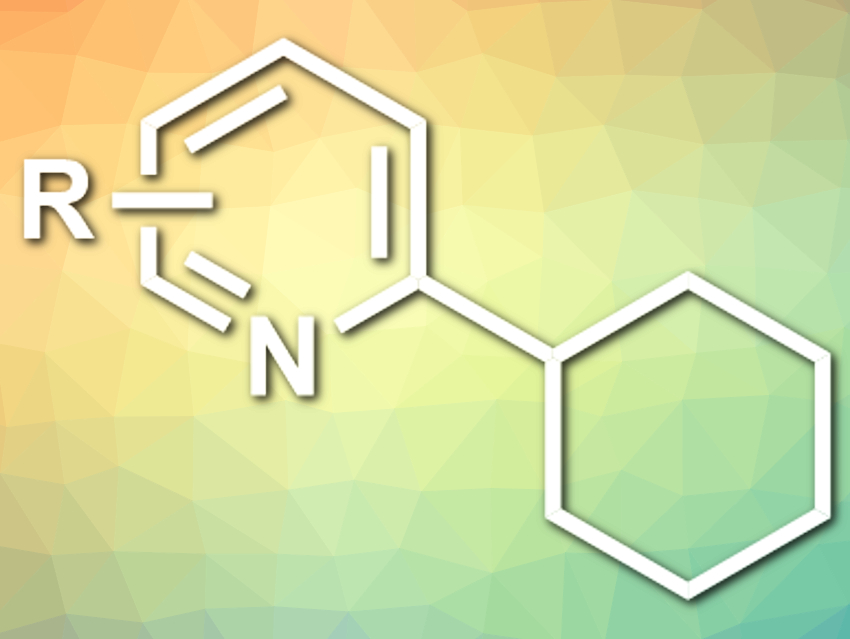
The oxidative coupling between two compounds with C–H bonds is a general approach to creating C–C bonds. It can, for example, be used for the synthesis of alkylated heteroaromatic compounds. This reaction usually is performed using both a photocatalyst and stoichiometric peroxides.
Aiwen Lei and colleagues, Wuhan University, China, have developed a visible-light-induced selective C(sp3)–H arylation with heteroarenes (example product pictured), mediated by Selectfluor. Selectfluor or N-Chloromethyl-N‘-fluorotriethylenediammonium bis(tetrafluoroborate) is usually used as a fluorination reagent and oxidant. The team found that the compound can be activated by blue LED light to give a radical cation centered at nitrogen. This radical can abstract a hydrogen atom from, e.g., an alkane to induce the coupling with a heteroarene. This step is followed by a one-electron oxidation to give the final product.
The team used this approach to couple different cycloalkanes, ethers, or aryl-substituted alkanes with heteroarenes such as quinolines or benzothiazoles. The desired products were obtained in good to excellent yields. The reaction can be performed on a gram scale and needs no external photocatalysis.
- Visible-Light-Induced C(sp3)–H Oxidative Arylation with Heteroarenes,
Xing-An Liang, Linbin Niu, Shengchun Wang, Jiamei Liu, Aiwen Lei,
Org. Lett. 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.9b00744