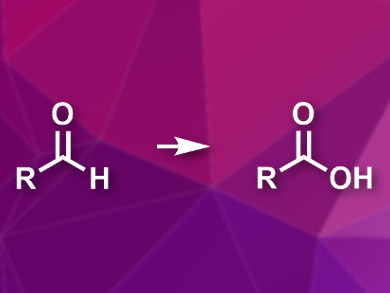
Aldehydes can be converted into carboxylic acids by oxidation. The are several useful protocols for this reaction, but they usually require stoichiometric amounts of expensive and/or hazardous oxidants. Using molecular oxygen would be a cheaper, greener alternative, but this generally requires a transition-metal catalyst.
Peng-Fei Dai, Yan-Biao Kang, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, and Jian-Ping Qu, Nanjing Tech University, China, have developed the first example of an organocatalyzed aerobic oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids in both organic solvents and water under mild conditions. the team used 5 mol % of N-hydroxyphthalimide as the organocatalyst and O2 as the only oxidant.
The reaction proceeds with high yields in acetonitrile or water. No transition-metal catalysts or expensive stoichiometric oxidants are required. The protocol tolerates a range of functional groups on the aldehyde, including ketones, halogens, aryl substituents, and carbamates.
- Organocatalyzed Aerobic Oxidation of Aldehydes to Acids,
Peng-Fei Dai, Jian-Ping Qu, Yan-Biao Kang,
Org. Lett. 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.9b00101