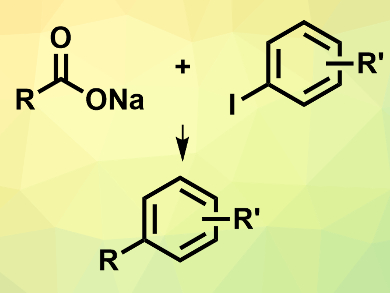
Inexpensive alkyl carboxylic acids can be coupled with aryl halides to provide new carbon skeletons, e.g., for drug discovery. However, such cross-coupling reactions often require expensive catalysts, hazardous reagents, or several steps. Jon Loren and colleagues, Genomics Institute of the Novartis Research Foundation, San Diego, CA, USA, have developed a one-pot electrochemical nickel-catalyzed decarboxylative cross-coupling reaction between alkyl carboxylates and aryl halides (pictured).
The team used N-hydroxyphthalimide tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate (PITU) to convert the carboxylates into redox-active N-hydroxyphthalimide esters in situ. The coupling reactions between the generated ester and the aryl halide were then performed using electrochemical conditions at room temperature in N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA). NiCl2dme (dme = dimethoxyethane) was used as the catalyst and 4,4′-di-tert-butyl-2,2′-bipyridine (dtbbpy) as a ligand.
The desired products were obtained in isolated yields of up to 95 %. The reaction tolerates primary and secondary carboxylates and a range of functionalized aryl iodides, with higher yields for aryl iodides with electron-withdrawing groups.
- One-Pot Electrochemical Nickel-Catalyzed Decarboxylative sp2–sp3 Cross-Coupling,
Takaoki Koyanagi, Ananda Herath, Ashley Chong, Maxim Ratnikov, Andrew Valiere, Jim Chang, Valentina Molteni, Jon Loren,
Org. Lett. 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.8b04090