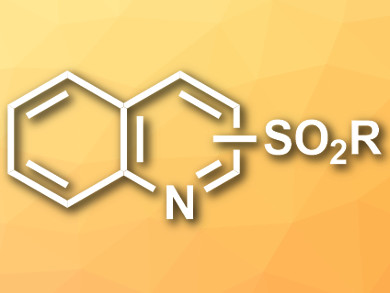
Sulfonylated N-heteroaromatics (example pictured) have applications, e.g, in organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and functionalized materials. Common methods for their synthesis suffer either from low regioselectivity or from a need for costly and environmentally harmful reagents.
Wei-Min He, Hunan University of Science and Engineering, Yongzhou, China, and Hunan University, Changsha, China, and colleagues have developed a green reaction protocol for the synthesis of sulfonylated N-heteroaromatics that is practical, metal-free, and organic-solvent free, produces minimal waste, uses readily available reagents, and proceeds under mild conditions. The team used halogenated or sulfonated N-heteroaromatics as starting materials, sulfonyl chlorides as reagents, Na2SO3 as a reductant, and water as a solvent.
The desired products were obtained in good to excellent yields and could easily be isolated via filtration and washing. The reaction is chemoselective and regioselective and has a broad substrate scope. The researchers propose a mechanism that involves a slow reduction of the sulfonyl chloride by Na2SO3 to form a sodium sulfinate salt. The halogenated or sulfonated N-heteroaromatic reagent is activated by a proton and attacked by the sulfinate. A final deprotonation step gives the product.
- Waste-Minimized Protocol for the Synthesis of Sulfonylated N-Heteroaromatics in Water,
Long-Yong Xie, Sha Peng, Jia-Xi Tan, Rong-Xia Sun, Xianyong Yu, Ning-Ning Dai, Zi-Long Tang, Xinhua Xu, Wei-Min He,
ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b04339



![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)