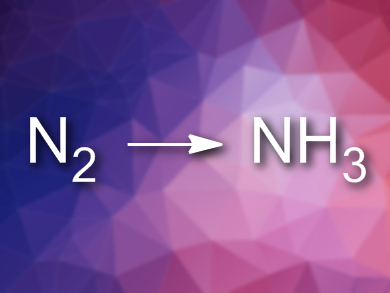
The fixation of nitrogen to produce ammonia is performed on a large scale using the very energy-intensive Haber-Bosch process. This process requires high temperatures and pressures. The electrochemical fixation of N2 under ambient conditions could be an alternative, but requires improved electrocatalysts for the N2 reduction reaction (NRR).
Tingshuai Lie, Xuping Sun, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Sichuan, and colleagues have developed an efficient electrocatalyst for the NRR, composed of cubic SnO2 sub-micron particles on a carbon cloth (SnO2/CC). The team prepared the catalyst by immersing a strip of CC in an aqueous solution of SnCl4 and NaOH and heating it to 200 °C for 24 h.
The prepared catalyst achieves a large NH3 yield of 1.47·10–10mol s–1 cm–2 at –0.8 V and a high Faradaic efficiency of 2.17 % at –0.7 V, outperforming many other NRR electrocatalysts. SnO2 combines a low cost, low toxicity, and high chemical stability, which makes Sn-based catalysts promising for nitrogen fixation.
- Ambient NH3 synthesis via electrochemical reduction of N2 over cubic sub-micron SnO2 particle,
Ling Zhang, Xiang Ren, Yonglan Luo, Xifeng Shi, Abdullah M. Asiri, Ting Shuai Li, Xu-Ping Sun,
Chem. Commun. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc06524a