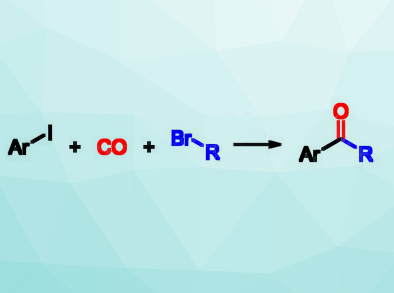
Unsymmetrical ketones, e.g., alkyl aryl ketones (pictured right), have a wide range of applications in the chemical industry and can also be further transformed into other useful compounds using reactions at their carbonyl group. Usually, alkyl aryl ketones are prepared by a Friedel‐Crafts acylation of arenes, However, this requires electron‐rich arenes and stoichiometric amounts of Lewis acid.
Xiao‐Feng Wu, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou, China, and University of Rostock, Germany, and colleagues have developed an efficient carbonylative cross‐coupling of aryl iodides and unactivated alkyl bromides to give alkyl aryl ketones. The team reacted the alkyl iodides and alkyl bromides with CO, which was produced from formic acid in a so-called In-Ex tube. This type of tube is a special apparatus combining two reaction vessels, one for the production of a gas and one for the intended reaction. This setup improves the safety when handling toxic gases like CO. In addition to the substrates, the reaction requires Pd2(dba)3 (dba = dibenzylideneacetone) as a catalyst, PPh3 as a ligand, and Mg/ZnCl2 to form intermediate alkylmagnesium and alkylzinc bromides. It is performed in tetrahydrofuran (THF) at 55 °C for 12 h.
A variety of alkyl aryl ketones were synthesized in moderate to excellent yields. Both primary and secondary alkyl bromides were suitable coupling partners for the reaction. The mechanism involves an oxidative addition of the aryl iodide to the Pd catalyst, followed by the insertion of CO and the reaction with the alkylzinc compounds formed in situ. These alkylzinc compounds are formed from the alkyl bromide via an alkylmagnesium intermediate. Zinc alone was not reactive enough for this approach. According to the researchers, the developed method can also be used for the late‐stage functionalization of natural products and complex molecules.
- Palladium-Catalyzed Carbonylative Coupling of Aryl Iodides with Alkyl Bromides: Efficient Synthesis of Alkyl Aryl Ketones,
Jin-Bao Peng, Bo Chen, Xinxin Qi, Jun Ying, Xiao-Feng Wu,
Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201800879