The pleurospiroketals A (pictured) and B are sesquiterpenoids that were first discovered in the edible mushroom Pleurotus cornucopiae (branched oyster mushroom). The compounds have potentially useful biological activities, such as cytotoxicity against HeLa cancer cells. No total syntheses of these two molecules had been achieved so far.
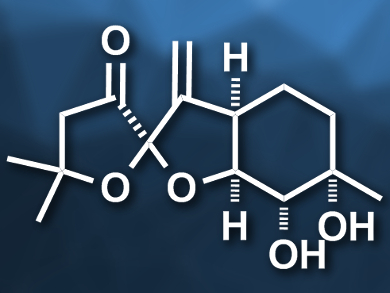
Hisanaka Ito, Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Sciences, Japan, and colleagues have performed the first asymmetric total synthesis of pleurospiroketals A and B. The team started from a known carboxylic acid (5-methyl-5-hexenoic acid) and introduced (S)-4-isopropyloxazolidinone as a chiral auxiliary. Then they performed a syn-selective Evans aldol reaction of the resulting product with acrolein. The resulting diene was subjected to a ring-closing metathesis reaction using a Grubbs second-generation catalyst to give a six-membered ring (pictured on the right). The chiral auxiliary was then converted to a methyl ketone and the C=C double bond in the six-membered ring was diastereoselectively dihydroxylated using potassium osmate. The spiroketal (pictured on the left) was created by converting the intermediate to a diketone precursor, which was treated with hydrochloric acid to induce the spiroketalization.
The synthesis gives the pleurospiroketals A and B as a 1:1 mixture in 16 steps. The two compounds can be separated using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). According to the researchers, the developed approach could also be used for the synthesis of other pleurospiroketals and structurally similar terpenoids.
- Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Pleurospiroketals A and B,
Toyoharu Kobayashi, Konomi Tanaka, Masako Ishida, Natsumi Yamakita, Hideki Abe, Hisanaka Ito,
Chem. Commun. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc06185h