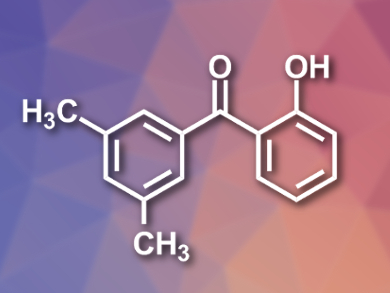
The Friedel-Crafts acylation, an electrophilic aromatic substitution with electronic-controlled regioselectivity, is a commonly used method to synthesize aryl ketones. Although regioselective arene acylation using other approaches is possible, it usually requires multiple steps and precious-metal catalysts.
Christopher J. Douglas and colleagues, University of Minnesota—Twin Cities, Minneapolis, USA, have developed a new method for the sterically controlled regioselective acylation of arenes and heteroarenes (example product pictured). The team used phenyl salicylates as the acylation reagents, [Ir(cod)OMe]2 (cod = 1,5-cyclooctadiene) as a catalyst, and rac-2-(di-tert-butylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthyl as a ligand. The reactions were performed in the respective arenes or heteroarenes, which were used in solvent quantities, at 170 °C.
The reaction tolerates a broad range of functional groups on the salicylate ester. Simple electron-rich arenes as substrates react particularly well under the conditions. The researchers suggest that the sterically controlled acylation is achieved via a concerted metalation–deprotonation C–H activation. The developed reaction offers substitution patterns previously inaccessible in a single step. The method’s usefulness was demonstrated by a concise synthesis of the anticancer agent hydroxyphenstatin.
- Integrating Metal-Catalyzed C–H and C–O Functionalization To Achieve Sterically Controlled Regioselectivity in Arene Acylation,
Nicholas A. Serratore, Constance B. Anderson, Grant B. Frost, Truong-Giang Hoang, Steven J. Underwood, Philipp M. Gemmel, Melissa A. Hardy, Christopher J. Douglas,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b06476