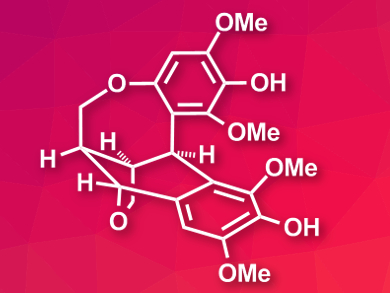
Lignans are organic compounds found in many plants. They have diverse biological effects such as anticancer, antiviral, or antioxidant activity. Ovafolinins, a family of lignans, were discovered in Lyonia ovalifolia var. elliptica, a type of tree found in Asia. Ovafolinins A (pictured) and B have very similar frameworks, differing only in the opening or closing of a tetrahydrofuran ring.
Xiangdong Hu and colleagues, Northwest University, Xi’an, China, have developed an asymmetric total synthesis of (+)-ovafolinins A and B. The team started from an (S)-Taniguchi lactone, which was alkylated in a stereoselective reaction using a functionalized benzyl bromide. The lactone was then opened and the resulting ester was reduced. The product was reacted with a functionalized phenol in a Mitsonobu transformation. The intermediate was then subjected to a vinyl oxidation to produce an aldehyde group. Treatment of the product with trifluoroacetic acid and a final hydrogenation to remove all benzyl ether protecting groups gave (+)-ovafolinin B. This product could be converted to (+)-ovafolinin A using a Cu(OAc)2-catalyzed benzylic oxidative cyclization.
The total synthesis of (+)-ovafolinin B involved 11 steps and gave a total yield of 23 %; the synthesis of (+)-ovafolinin A needed one additional step and gave 21 % total yield. According to the researchers, this makes the approach an efficient asymmetric synthetic route to these compounds.
- Asymmetric Total Synthesis of (+)-Ovafolinins A and B,
Xianhe Fang, Lei Shen, Xiangdong Hu,
Chem. Commun. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc03456g



![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)