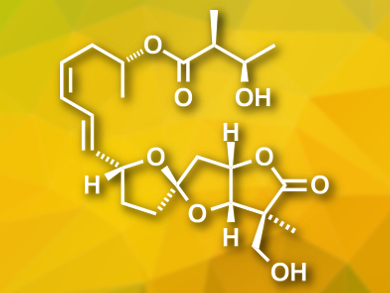
Ascospiroketals A and B were isolated from the marine fungus Ascochyta salicorniae. The compounds contain a rare tricyclic core with a 5,5-spiroketal-γ-lactone. There are similar compounds featuring this structure that are bioactive, and thus, ascospiroketals are expected to show biological activities, as well.
Hiroaki Miyaoka and colleagues, Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Sciences, Japan, have performed an asymmetric total synthesis of ent-ascospiroketal B. It was their goal to determine the absolute configuration of ascospiroketal B and allow the study of the compound’s biological activity. The team started from a thioacetal and a tartaric acid derivative, which were connected and converted to a spiroketal with an epoxide group. A stereoselective reaction at this epoxide was used to create an asymmetric quarternary carbon center. Next, the γ-lactone moiety was formed and a iodovinyl group was introduced. A final Sonogashira coupling was used to give the desired product.
The researchers used 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy to characterize the product and found an excellent correlation between their data and that of the natural product. The biological activity of ent-Ascospiroketal B is under investigation.
- Total Synthesis of ent-Ascospiroketal B,
Yoshiyori Hara, Tatsuya Honda, Kazuto Arakawa, Koichiro Ota, Kazuo Kamaike, Hiroaki Miyaoka,
J. Org. Chem. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.7b02925