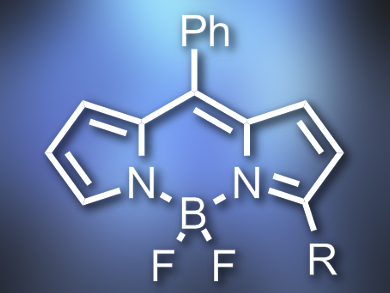
Boron dipyrromethene (BODIPY) dyes often have excellent spectroscopic and photophysical properties. They can be functionalized either by synthesis from suitable pyrroles, by postfunctionalization of reactive BODIPYs, or by direct C–H functionalization of BODIPY dyes.
Lijuan Jiao, Anhui Normal University, Wuhu, China, Noël Boens, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Belgium, and colleagues have developed a cross-dehydrogenative coupling (CDC) reaction, which can be used to functionalize the α-position of BODIPY dyes in a highly regioselective way. The team started from a range of BODIPY dyes and coupled them with allylic alkenes or ethers using a catalyst system consisting of tetrabutylammonium iodide (Bu4NI) and tert-butylhydroperoxide (tBuOOH, TBHP). They obtained α-functionalized alkenes (example pictured) which were previously difficult to access.
The proposed reaction mechanism involves the oxidation of Bu4NI with TBHP. The resulting species abstracts hydrogen from an allylic alkene, leading to the formation of an allylic radical. This radical reacts with a double bond in the BODIPY core. The intermediate formed in this reaction abstracts a hydrogen atom from another molecule of the allylic alkene. Finally, the product is oxidized to give the desired functionalized dye.
- Bu4NI/tBuOOH catalyzed, α-regioselective cross-dehydrogenative coupling of BODIPY with allylic alkenes and ethers,
Yang Yu, Lijuan Jiao, Jun Wang, Hua Wang, Changjiang Yu, Erhong Hao, Noël Boens,
Chem. Commun. 2017.
DOI: 10.1039/c6cc08098g