Ruthenium catalysts have a range of applications in racemizations and (transfer) hydrogenations. Understanding the mechanisms behind these reactions could lead to improved design and better catalysis.
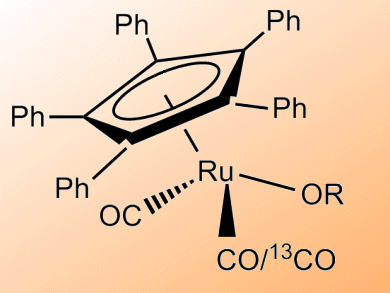
Jan Bäckvall and co-workers, Stockholm University, Sweden, have studied the CO exchange that occurs with two Ru catalysts: (η5-Ph5C5)Ru(CO)2Cl and (η5-Ph5C5)Ru(CO)2(Ot-Bu). The catalysts were employed in the racemization of sec-alcohols, and inclusion of 13CO was monitored by 13C NMR. CO exchange was shown to be 20 times faster for the active tert-butoxide complex than the ruthenium chloride precursor complex.
Addition of CO was also shown to result in a reduction in the rate of (S)-1-phenylethanol racemization, supporting the idea that reversible CO dissociation is a key step in the racemization mechanism of sec-alcohols with these type of Ru catalysts.
- CO Dissociation Mechanism in Racemization of Alcohols by a Cyclopentadienyl Ruthenium Dicarbonyl Catalyst
M. C. Warner, O. Verho, J.-E. Bäckvall,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011.
DOI: 10.1021/ja1098066