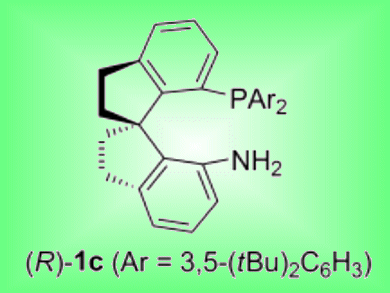
Iridium complexes with chiral spiro aminophophine ligands have been demonstrated to be highly efficient catalysts for the asymmetric hydrogenation of alkyl aryl ketones by Qi-Lin Zhou and co-workers, Nankai University, China.
Complexes with 3,5-di-tert-butylphenyl groups on the P atom were especially effective. A series of chiral alcohols were synthesized with up to 97 % ee, high turnover numbers (up to 10 000) and high turnover frequency (up to 3.7×104 h−1). The active catalyst was shown to be an iridium dihydride species containing one chiral spiro aminophosphine ligand, which was slowly transformed to an inactive iridium dihydride complex with two ligands.
These complexes have high potential for other asymmetric hydrogenation reactions as well as those of alkyl aryl ketones.
- Chiral Iridium Spiro Aminophosphine Complexes: Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Simple Ketones, Structure, and Plausible Mechanism
J.-B. Xie, J.-H. Xie, X.-Y. Liu, Q.-Q. Zhang, Q.-L. Zhou,
Chem. Asian J. 2011.
DOI: 10.1002/asia.201000716