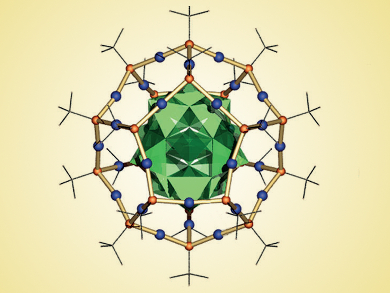
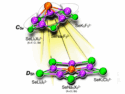
Polyoxometalates can be used as templates for the synthesis of high-nuclearity silver cluster systems.
Shuang-Qun Zang, Guang-Gang Hao, and colleagues at Zhengzhou University and Jiamusi University, both China, have come up with a core–shell cluster formed by self-assembly of metavanadate and silver(I) salts. The cluster comprises a C2h dodecahedrane-like [Ag30(tBuS)20]10+ unit that encapsulates a [VV10VIV2O34]10– core.
Upon acidification, the core transforms to a higher–symmetry D3d configuration and the color of the complex changes from dark yellow to green. Further treatment with base leads to a core–shell species virtually identical to the starting compound. The structural transformation was studied by using single-crystal X–ray crystallography, which is rare for this type of system. This work provides new insights into the behavior and properties of core–shell clusters.
- Acid-Base-Triggered Structural Transformation of a Polyoxometalate Core Inside a Dodecahedrane-like Silver Thiolate Shell,
Hong Liu, Chao-Yu Song, Ren-Wu Huang, Yu Zhang, Hong Xu, Mei-Jia Li, Shuang-Quan Zang, Guang-Gang Gao,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201511765