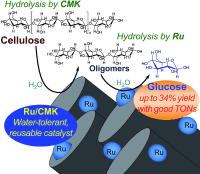
Cellulose is the most abundant nonfood biomass resource produced via photosynthesis. The hydrolysis of cellulose produces glucose, which is a versatile precursor to fuel, plastics, pharmaceuticals, and other value-added chemicals. However, the efficient hydrolysis of cellulosed to glucose with low environmental impact remains a challenge.
Hirokazu Kobayashi, Tasuku Komanoya, Kenji Hara, and Atsushi Fukuoka, Hokkaido University, Japan, studies the cellulose hydrolysis by supported metal catalysts without the use of sulfonic acid groups.
Ru/CMK-3 (mesoporous carbon materials, CMK) is a water-tolerant and reusable catalyst for the hydrolysis of cellulose, and exhibits high glucose yields and turnover numbers due to a synergistic effect between CMK-3 and Ru. CMK-3 contributes to the conversion of cellulose into oligosaccharides, while Ru promotes the hydrolysis of oligosaccharides to glucose.
- Water-Tolerant Mesoporous-Carbon-Supported Ruthenium Catalysts for the Hydrolysis of Cellulose to Glucose,
Hirokazu Kobayashi, Tasuku Komanoya, Kenji Hara, Atsushi Fukuoka,
ChemSusChem 2010, 3 (4), 440-443.
DOI: 10.1002/cssc.200900296