Aromatic aldehydes are vital chemical intermediates for the synthesis of various biologically active compounds. Their traditional synthetic methods, such as reduction of carboxylic acids or esters, suffer from harsh reaction conditions and poor selectivities. To overcome these issues, metal-catalyzed formylations of aromatic halides with CO have been developed and provide much simpler and selective ways to aromatic aldehydes.
However, these methods are limited by the use of highly toxic CO gas and the associated safety concerns. As an alternative, CO-free carbonylation reactions have attracted great attention. A number of reports describe the use of CO surrogates, such as paraformaldehyde and N-formylsaccharin, with metal catalysis, but the use of expensive ligands and formation of by-products are still drawbacks. Hence, a convenient, simple, and inexpensive route to aromatic aldehydes is still desired.
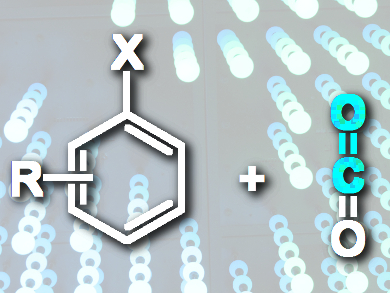
Zhimin Liu and colleagues, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, have developed a Pd-catalyzed method for the formylation of aryl halides with CO2 gas. The reaction utilizes a simple combination of a phosphine-chelated Pd catalyst and base, leading to aryl aldehydes in moderate to excellent yields and without any by-products in most cases. This approach is simple, cost-efficient, and environmentally friendly, and also widens the applications of CO2 to form value-added chemicals by the construction of new C–C bonds.
.png)
- An Efficient and General Method for Formylation of Aryl Bromides with CO2 and Poly(methylhydrosiloxane),
Bo Yu, Zhenzhen Yang, Yanfei Zhao, Leiduan Hao, Hongye Zhang, Xiang Gao, Buxing Han, Zhimin Liu,
Chem. Eur. J. 2015.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201504320