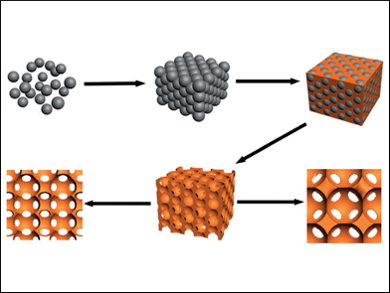
Organometal halide perovskites (OHPs) have gained interest as materials for the field of photovoltaics. The preparation of OHPs with highly hierarchical architectures and the morphology-controlled synthesis of OHPs to improve their performance are still challenging. Fabricating OHPs in inverse opal morphology may improve the performance of the materials in solar cells, lasers, and OLEDs.
Harun Tüysüz and Kun Chen, Max Planck Institute for Coal Research, Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, prepared a series of OHPs in inverse opal morphology by using a colloidal crystal templating method. Polystyrene (PS) microspheres were used to fabricate the artificial opal templates. The mild, scalable, and flexible method is compatible with different halides and organometallic ammonium compositions.
The perovskite inverse opals allow band gap engineering, show sensitive photocurrent generation, and could be promising for optoelectronic devices and photocatalysis.
- Morphology-Controlled Synthesis of Organometal Halide Perovskite Inverse Opals,
Kun Chen, Harun Tüysüz,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201506367