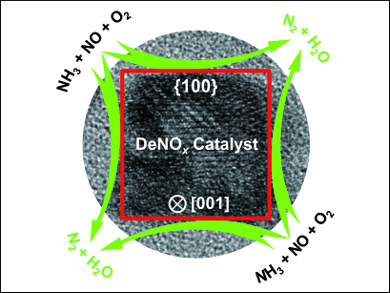
Selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides by ammonia (SCR) is an important way to control NOx emissions, which can result from fuel combustion and cause smog and acid rain. Manganese oxides are the most active known catalysts for low-temperature SCR. However, owing to the diversity and complexity of the surface structures of manganese oxides, little is known about their catalytically active sites (CASs).
Xingfu Tang and colleagues, Fudan University, Shanghai, China, have combined electron microscopy, X-ray absorption spectroscopy, synchrotron X-ray diffraction, and reactivity studies to probe the CASs of a rod-shaped hollandite manganese oxide SCR catalyst.
The CAS is shown to consist of a semi-tunnel structure formed by surface lattice oxygen, which facilitates the adsorption and activation of NH3. Such accurate identification of CASs will aid in the investigation of the SCR reaction mechanism and, in turn, enable design of more efficient SCR catalysts in the future.
- The Active Sites of a Rod-Shaped Hollandite DeNOx Catalyst,
Pingping Hu, Manfred Erwin Schuster, Zhiwei Huang, Fei Xu, Shifeng Jin, Yaxin Chen, Weiming Hua, Dang Sheng Su, Xingfu Tang,
Chem. Eur. J. 2015.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201501084