Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have a number of attractive properties, and have many applications such as in drug delivery, imaging, and sensors. There are, however, very few reports on the synthesis of cationic AuNPs.
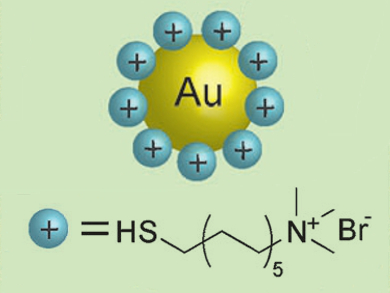
Robin H. Ras and colleagues, Aalto University, Finland, designed a quick and simple procedure that results in cationic AuNPs with tunable sizes.The researchers synthesized water-soluble citrate-capped AuNPs using a standard procedure. They transferred the nanoparticles to toluene by addition of octadecylamine. The resulting neutral nanoparticles were then made cationic by treatment with thiol ligands bearing quaternary ammonium groups (pictured).
The synthesis strategy is based on the strength of the ligand interactions with the AuNPs: the citrate ligands are only electrostatically bound, the amine ligand binds more strongly, and the thiol ligand binds even more strongly and forms a covalent bond with the gold. Attempts to directly produce cationic nanoparticles from citrate-capped nanoparticles resulted in precipitation of the AuNPs.
The cationic AuNPs are highly stable and can be made in sizes ranging from 8 to 20 nm. They also have a stronger surface-plasmon absorption than other cationic nanoparticles. In the presence of the cowpea chlorotic mottle virus, the cationic AuNPs self-assembled to form electrostatically bound complexes. The cationic AuNPs thus have potential as components in biotemplated assemblies or in applications where a strong localized surface plasmon resonance is required.
- Rapid Cationization of Gold Nanoparticles by Two-Step Phase Transfer,
Jukka Hassinen, Ville Liljeström, Mauri A. Kostiainen, Robin H. A. Ras,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201503655


![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)