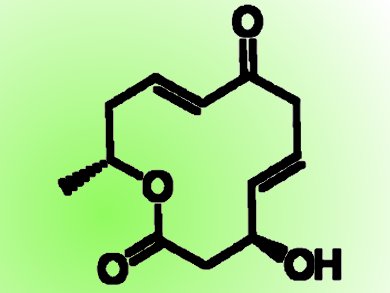
Dendrodolides, a class of 12-membered macrolides, were recently isolated from Dendrodochium Sp., a fungus associated with the sea cucumber Holothurian nobilis Selenka, which was collected from the South China Sea. Dendrodolides have different levels of growth-inhibiting activity against human hepatocarcinoma (SMMC-7721) and human colon cancer (HCT116) cells in in-vitro bioassays.
Debendra K. Mohapatra and colleagues, CSIR-Indian Institute of Chemical Technology, Hyderabad, India, have developed a unified synthetic strategy for the total synthesis of the dendrodolide family in a highly convergent and stereoselective manner. The synthetic strategy starts with commercially available materials and involves the enantioselective epoxidation of trans-crotanaldehyde and regioselective opening of an epoxide with a Pd catalyst (Jørgensen asymmetric epoxidation), asymmetric allylation (Keck and Brown allylation), Yamaguchi esterification, and ring-closing metathesis as key steps.
.jpg)
- A Unified Synthetic Strategy for Dendrodolides E, F, G, I, J, and L,
Debendra K. Mohapatra, D. Prabhakar Reddy, Srinivas Gajula, Karthik Pulluri, J. S. Yadav,
Asian J. Org. Chem. 2015.
DOI: 10.1002/ajoc.201500037