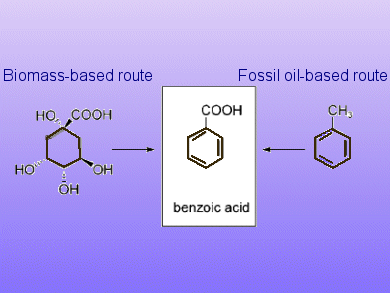
A simple one-step procedure to efficiently and selectively produce benzoic acid from the renewable starting materials shikimic acid and quinic acid by using a formic acid-mediated dehydroxylation method is described by Elena Arceo, Jonathan Ellman, and Robert Bergman from the University of California, Berkley.
For the deoxygenation of quinic acid, the reaction temperature was heated to 220 °C affording benzoic acid in 92 % yield. For the conversion of shikimic acid, the reaction temperature could be lowered to 190 °C affording the product in 89 % after extraction.
Exploiting biomass resources for the production of aromatic hydrocarbons could provide a sustainable alternative to the traditional petroleum-based manufacture and also avoids the use of benzene-based substances hazardous to human health and the environment.
- A Direct, Biomass-Based Synthesis of Benzoic Acid: Formic Acid-Mediated Deoxygenation of the Glucose-Derived Materials Quinic Acid and Shikimic Acid
E. Arceo, J. Ellman, R. Bergman,
ChemSusChem 2010, 3.
DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201000111



![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)