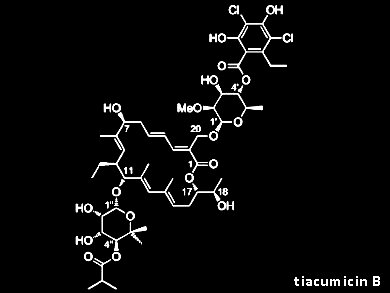
Tiacumicin B (lipiarmycin A3, fidaxomicin) is an atypical macrolide antibiotic. It inhibits bacterial RNA polymerase and is used for the treatment of infections with Clostridium difficile, the most frequent cause of nosocomial diarrhea infections in the developed world. Tiacumicin B is also a potent inhibitor of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but due to its limited oral bioavailability is unsuitable for systemic therapy.
Despite their biological profiles and intriguing structures, no total synthesis of any member of the tiacumicin/lipiarmycin/clostomicin family or the corresponding aglycones has been reported to date.

Florian Glaus and Karl-Heinz Altmann, ETH Zurich, Switzerland, have developed an efficient synthesis of the tiacumicin B aglycone.
The synthesis contains a high-yielding intramolecular Suzuki cross-coupling reaction for macrocyclic ring closure. Key steps in the synthesis of the macrocyclization precursor were a highly selective, one-pot Corey–Peterson olefination, which is based on a new thiophenol-mediated Z → E isomerization of an α, β-unsaturated corss-etathesis reaction, and an ene–diene cross-metathesis reaction.
Depending on the reaction conditions, the final deprotection leads to either the fully deprotected tiacumicin B aglycone or partially protected versions thereof.
- Total Synthesis of the Tiacumicin B (Lipiarmycin A3/Fidaxomicin) Aglycone,
M. Sc. Florian Glaus, Prof. Karl-Heinz Altmann,,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201409510