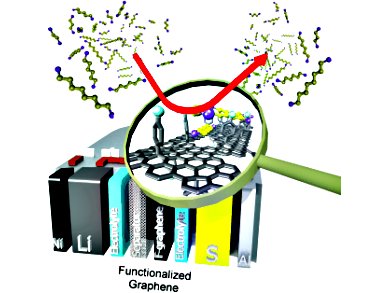
Rechargeable batteries play an important role in bridging the gap between old disruptive technologies and new alternative technologies for efficient energy conversion. However, the low storage capacity of batteries remains a problem. The energy-density limitations of lithium-ion batteries triggered the evolution of new systems, including lithium-sulfur batteries, which have a superior energy density. Although many studies have focused on improving lithium-sulfur batteries, little attention has been devoted to the optimization of the electrode separator.
Robert Dominko, National Institute of Chemistry, Slovenia, and his co-workers demonstrate that a thin layer of chemically modified reduced graphene oxide (rGO) can be used as an interlayer between the lithium anode and the sulfur cathode in lithium-sulfur batteries. The use of hydrophobic rGO as a separator improves the capacity retention of the lithium-sulfur battery, as it effectively reduces the reactivity of long-chain polysulfides with the metallic lithium, leading to more homogeneous precipitation of the end-discharge products during continuous cycling.
Effective separation of the sulfur cathode and lithium anode leads to stable lithium-sulfur battery cycling with very high coulombic efficiency. This helps towards the development of new and effective technologies to eliminate the use of fossil fuels and outdated technologies.
- Effective Separation of Lithium Anode and Sulfur Cathode in Lithium-Sulfur Batteries,
Alen Vizintin, Manu U. M. Patel, Bostjan Genorio, Robert Dominko,
ChemElectroChem 2014, 6.
DOI: 10.1002/celc.201402039