Carbazole alkaloids are an interesting research target because of their useful biological activities and structural variety. A broad range of oxygenated pyrano[3,2-a]- and pyrano[2,3-a]carbazoles have been isolated by Furukawa, Wu, and others from plants of the genera Murraya and Clausena belonging to the family Rutaceae. Whilst many synthetic approaches to pyranocarbazoles have been developed, only a few routes to the more highly oxygenated derivatives have ever been reported.
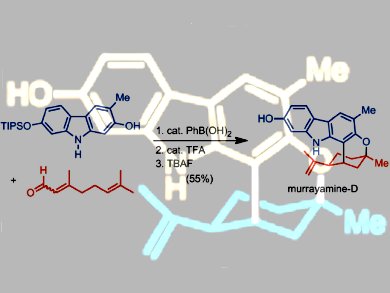
To address this shortage, Hans-Joachim Knölker and co-workers, Technische Universität Dresden, Germany, have developed an efficient access to a broad range of 7- and 8-oxygenated pyrano[3,2-a]- and pyrano[2,3-a]carbazole alkaloids. For eight of these alkaloids, the group describes the first total synthesis: murrayamine A (mukoenine C), mahanine, murrayamine B, D, and H, and clauszoline G, B, and H. Key steps in the synthesis feature a palladium-catalyzed construction of the carbazole nucleus and a boronic acid catalyzed annulation of the pyran ring.
A more detailed investigation into the promising pharmacological properties of these compounds is now feasible.
- Total Synthesis of 7- and 8-Oxygenated Pyrano[3,2-a]carbazole and Pyrano[2,3-a]carbazole Alkaloids via Boronic Acid Catalyzed Annulation of the Pyran Ring,
Konstanze K. Julich-Gruner, Olga Kataeva, Arndt W. Schmidt, Hans-Joachim Knölker,
Chem. Eur. J. 2014.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201403143



![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)