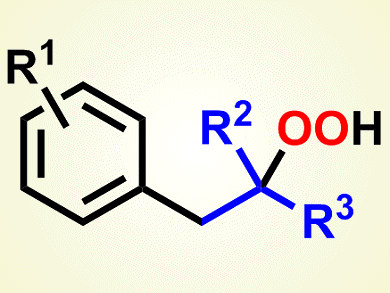
The Meerwein arylation, dating back to 1939, has become a highly versatile radical multicomponent reaction for the functionalization of alkenes. Recent advances in this arylation include the use of new aryl radical sources, such as bromo- and iodobenzenes, in addition to the traditionally used diazonium salts, and the tolerance of non-activated alkenes, as well as activated alkenes. Other than one single example with α-methylstyrene, all of the dioxygen-based reactions reported so far rely on the presence of a pure oxygen atmosphere.
Markus R. Heinrich and colleagues, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen–Nürnberg, Germany, report a new carbooxygenation-type version of the Meerwein arylation in which the introduction of oxygen has been achieved by using dioxygen from the air. To generate the required aryl radicals under oxidative reaction conditions, the team used phenyl hydrazines in combination with the strong oxidant manganese dioxide, which was used in its commercially available form.

The best results were obtained with α-substituted acrylates. The team found that, importantly, the aryl hydrazine has to be added slowly to the reaction mixture to allow sufficient uptake of dioxygen from the air.
- Manganese(IV)-Mediated Hydroperoxyarylation of Alkenes with Aryl Hydrazines and Dioxygen from Air,
Stephanie Kindt, Hannelore Jasch, Markus R. Heinrich,
Chem. Eur. J. 2014.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201400064


![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)
