Methylated amines are found in dyes, natural products, pharmaceuticals, and bulk and fine chemicals. However, most of the methylating reagents used in synthesis are toxic or carcinogenic and have issues of over methylation or limited substrate scope. Whilst there have been some efforts to address this problem, more effective, greener, and less toxic methods for these transformations are still highly desirable.
Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), a byproduct of the wood industry, is a cheap, versatile solvent with low toxicity that is widely used in organic synthesis and the pharmaceutical industry. Chao Wang, Jianliang Xiao, and co-workers, Shaanxi Normal University, China, and University of Liverpool, UK, have utilized this solvent under catalyst-free conditions for the development of a new amine methylation protocol with very broad substrate scope. Aromatic nitro compounds could also be directly transformed into dimethylated amines in the presence of a cheap iron catalyst.

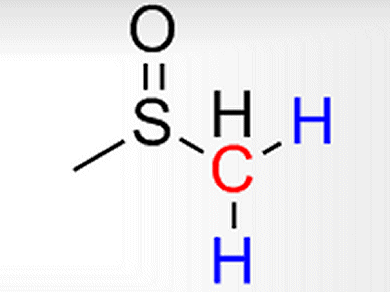
Mechanistic studies were also conducted that suggest that the methylation involves the transfer of a methylene group from DMSO to an amine and the reduction of the resulting imine by formic acid.
- A General Method for N-Methylation of Amines and Nitro Compounds with Dimethylsulfoxide,
Xue Jiang, Chao Wang, Yawen Wei, Dong Xue, Zhaotie Liu, Jianliang Xiao,
Chem. Eur. J. 2014.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201303802



![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)