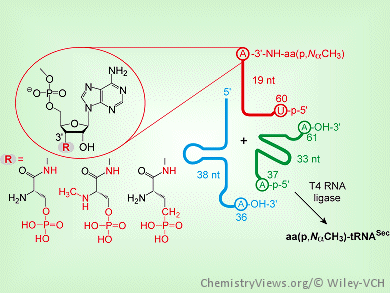
Selenocysteine (Sec) is the only amino acid that is synthesized on its cognate transfer RNA (tRNASec). Its biosynthesis involves the enzyme O-phosphoseryl-tRNA:selenocysteinyl-tRNA synthase (SepSecS). SepSecS is an enzyme that catalyzes the terminal chemical reaction during which the phosphoseryl–tRNASec intermediate is converted into selenocysteinyl-tRNASec.To further improve the understanding of the mechanism of the biosynthesis of Sec in general and the mechanism of SepSecS in particular, stable tRNASec substrates carrying aminoacyl moieties that mimic particular reaction intermediates are needed.
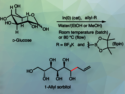
Miljan Simonović, University of Illinois, Chicago, Il, USA, Ronald Micura, Leopold-Franzens University, Austria, and co-workers have developed a synthesis for methylated, phosphorylated, and phosphonated serinyl-derived RNA conjugates together with the corresponding tRNASec mimics. The procedure allowed for efficient site-specific methylation and/or phosphorylation directly on the solid support utilized in the automated RNA synthesis. Finally, a three-strand enzymatic ligation protocol was developed to obtain the corresponding full-length tRNASec derivatives.
These tRNASec mimics are of interest for mechanistic studies as the modified amino acid moieties can interfere with discrete steps in the biosynthetic cycle of selenocysteine. The new mimics are also attractive for high-resolution crystallographic studies as the aminoacyl moieties are attached to tRNASec through a hydrolysis-resistant linkage.
- The Synthesis of Methylated, Phosphorylated, and Phosphonated 3′-Aminoacyl-tRNASec Mimics,
Lukas Rigger, Rachel L. Schmidt, Kaitlyn M. Holman, Miljan Simonović, Ronald Micura,
Chem. Eur. J. 2013.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201302188