Serine/threonine protein phosphatase 5 (PP5) is a member of the most abundant family of the protein serine/threonine phosphatases and it catalyzes dephosphorylation. In solution, PP5 is only active when it forms complexes with other proteins. Complexes involving PP5 have been described that affect the growth of cells and their response to stress, and a link between PP5 and cancer has been proposed. Despite numerous attempts to unravel the significance of PP5 in these pathways, its exact biological role remains unknown. Also, there is no consensus on the substrate-binding sequence for PP5, and its targets for dephosphorylation have not been identified.
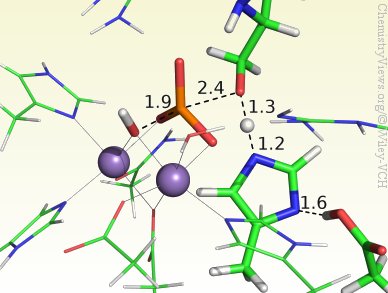
Although PP5 is known to have two metal ions in the active center, their identity is currently not clear. However, to determine the catalytic mechanism of PP5, Nino Russo and co-workers, Università della Calabria, Italy, have used a Mn–Mn-containing DFT cluster model that includes all relevant residues, the substrate, and the two Mn ions. The results show a concerted mechanism through an in-line transition state and no intermediates. The metal ions were found to have a mainly electrostatic role, whereas His304 and Asp274 stabilize the leaving group. Moreover, the ideal configuration was found to involve deprotonation of both the nucleophile and a second water molecule, giving the active center a charge of zero.
- The Catalytic Mechanism of Protein Phosphatase 5 Established by DFT Calculations,
António J. M. Ribeiro, Marta E. Alberto, Maria J. Ramos, Pedro A. Fernandes, Nino Russo,
Chem. Eur. J. 2013.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201301565