The use of a nanomaterial-based drug system provides the advantage of being able to penetrate cell membranes of rapidly dividing tumor cells, while at the same time having low cytotoxicity toward normal cells. The core of their nanocomposites contain boron or gadolinium, which has recently been explored for its usage in more efficient capture agents, owing to its high cross-sectional value for neutrons.
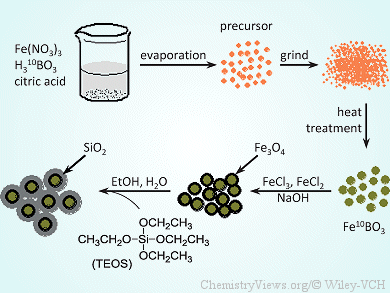
Narayan S. Hosmane, Northern Illinois University, USA, and co-workers synthesized nanocomposites of Fe10BO3/Fe3O4/SiO2 and GdFeO3/Fe3O4/SiO2 by a gel combustion technique using citric acid as fuel and chelation. The core of their nanocomposites contain boron or gadolinium, which has recently been explored for its usage in more efficient capture agents, owing to its high cross-sectional value for neutrons. An Fe3O4-coating is added for purposes of imaging and/or separation, and the additional silica shell for decreased toxicity and increased functionality.
The magnetic nanocomposites combine the advantages of silica and magnetic carrier technology. They exhibit strong magnetic properties, thus indicating that they might have potential applications in diagnostic analysis of cancer through use in neutron capture therapy.
 Synthesis and Characterization of Fe10BO3/Fe3O4/SiO2 and GdFeO3/Fe3O4/SiO2: Nanocomposites of Biofunctional Materials,
Synthesis and Characterization of Fe10BO3/Fe3O4/SiO2 and GdFeO3/Fe3O4/SiO2: Nanocomposites of Biofunctional Materials,
Shanmin Gao, Xin Liu, Prof. Tao Xu, Xuehua Ma, Zheyu Shen, Aiguo Wu, Yinghuai Zhu, Narayan S. Hosmane,
ChemistryOpen 2013, 3, 88–92.
DOI: 10.1002/open.201300007