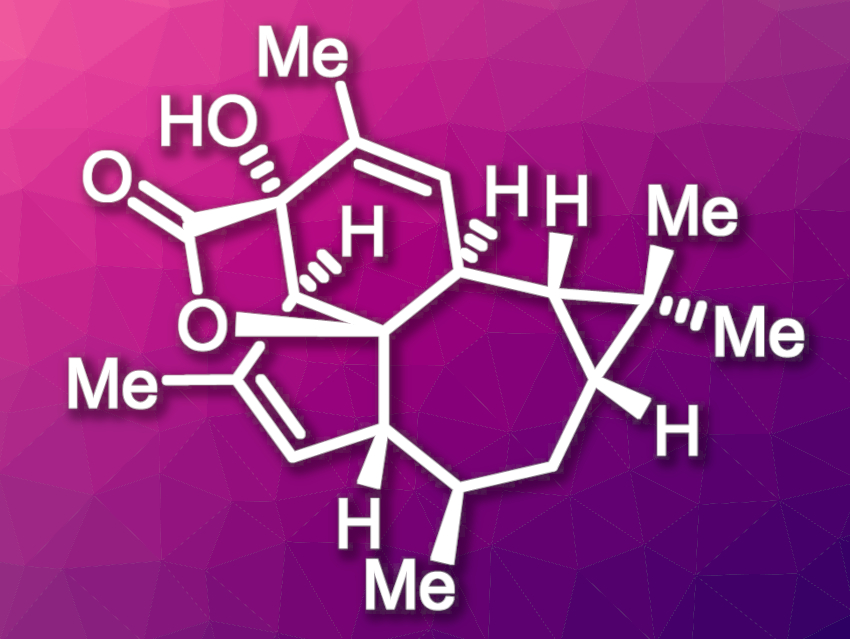
Euphorikanin A, a diterpenoid lactone, was isolated from the roots of Euphorbia kansui, which are used in traditional Chinese medicine. Euphorikanin A possesses a highly strained 5/6/7/3-fused tetracyclic skeleton with a bridged [3.2.1]-γ-lactone unit, and it features eight contiguous stereocenters. Preliminary bioactivity studies have shown that it has moderate cytotoxic activities against two human tumor cell lines.
Yanxing Jia, Peking University, Beijing, China, and colleagues have developed a bioinspired total synthesis of (+)-euphorikanin A. The team used a stereoselective alkylation and an aldol condensation to install the main stereocenters. An intramolecular nucleophile-catalyzed aldol lactonization was used to assemble the five-membered ring. The seven-membered ring was then constructed via a McMurry coupling reaction. Finally, a biomimetic benzylic-acid-type rearrangement formed the bridged [3.2.1]-γ-lactone moiety, giving (+)-euphorikanin A.
In total, the synthesis has 29 steps (longest linear sequence) and gives 4 % overall yield. According to the researchers, the synthetic approach offers the possibility for otherwise difficult to achieve structural modifications.
- Bioinspired Total Synthesis of (+)‐Euphorikanin A,
Zhuang Chen, Kuan Zhao, Yanxing Jia,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202200576