Vision of Wearable Electronics
Jackets with built-in mobile phones, sports clothes that warn you when your heart rate gets too high, wallpaper with glowing patterns—these are not concepts from a science fiction movie, some of them are actually already available, and they may soon become commonplace. These applications require electrically conductive fibrous materials. Korean researchers have now developed a new process for rendering paper and textile fibers conductive with aluminum.
Conventional silicon-based electronics are actually not very well-suited to wearable devices because they are brittle, cannot be bent or folded, and must not fall onto a hard surface. This makes “wearable” electronics unthinkable. But they would not just offer opportunities for fun and games, they could also be useful in many areas. They would allow the bodily functions of at-risk or chronically ill patients to be monitored without requiring them to walk around with cables attached to them. A baby’s sleepwear could sound an alarm if its breathing stops. “Intelligent” protective clothing could constantly indicate the position of field personnel by radio. Textile and paper electronics would also be ideal for novel large-scale interior design elements and security features in buildings.
These types of applications all require a flexible but conductive material that can be applied to a flexible substrate in the form of electronic circuits. Current techniques like printing or vapor deposition are not applicable to fibrous materials because it is not possible to produce a continuous pattern. In addition, these methods are very expensive.
Aluminum Coated Fibrous Materials
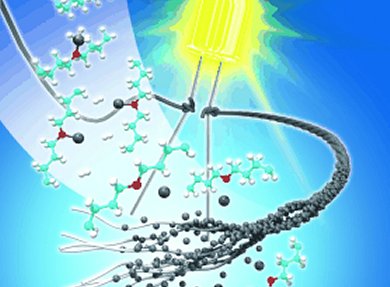
Researchers led by Hye Moon Lee at the Korea Institute of Materials Science and Seung Hwan Ko at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology have developed a simple, affordable approach for making conductive textile and paper fibers with aluminum. The paper or textile fibers are first pre-treated with a titanium-based catalyst and then dipped into a solution of an aluminum hydride composite solution. The catalyst is needed to allow the subsequent conversion of the aluminum compound to metallic aluminum to occur at room temperature.
The materials are not simply coated; in fact their fibers absorb the solution. This means that they do not have just a surface layer of aluminum, but are fully saturated. This produces papers and textile fibers with excellent electrical conductivity that can be bent and folded as desired. They can also be cut to any desired shape and size and simply glued or sewn onto an equally flexible support.
- Highly Conductive Aluminum Textile and Paper for Flexible and Wearable Electronics,
Hye Moon Lee, Si-Young Choi, Areum Jung, Seung Hwan Ko,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201301941