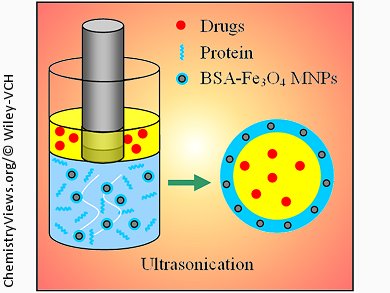
Protein microcapsules have been used effectively as drug delivery carriers for the treatment. Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), especially Fe3O4 MNPs, are of interest from a biomedical point of view owing to their good biocompatibility, strong superparamagnetism, nontoxicity, and easy preparation.
The group of Xuejun Cui, Jilin University, China, in collaboration with other groups at Jilin Agricultural University, China, and at the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces, Potsdam, Germany, have investigated how to combine protein microcapsules and magnetic nanoparticles to give magnetic drug-delivery carriers.
By using a sonochemical method, magnetic protein microcapsules (MPMCs) were easily prepared from bovine serum albumin (BSA) and Fe3O4 MNPs. The capsules could be easily manipulated to do oriented movement and aggregation by the use of external magnetic fields. In addition, the encapsulation of the hydrophobic, red fluorescent dye 5,10,15,20-tetraphenylporphyrin as a model drug into the MPMCs was readily achieved by dissolving the dye in soybean oil before the sonication process was applied.
- A Facile Sonochemical Route for the Fabrication of Magnetic Protein Microcapsules for Targeted Delivery,
X. Cui, Z. Li, S. Zhong, B. Wang, Y. Han, H. Wang, H. Möhwald,
Chem. Eur. J. 2013.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201301302