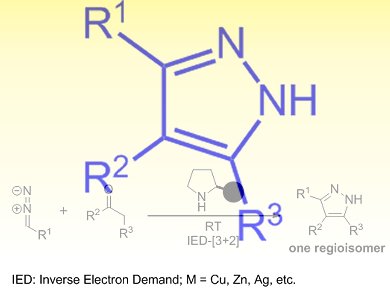
The pyrazole scaffold is found in many important pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and biologically active compounds. Commonly-used approaches for the synthesis of pyrazoles involve carcinogenic hydrazines or toxic transition metals, as well as a somewhat limited substrate scope and uncontrollable regioselectivity, which decrease their appeal.
Xiaojie Gong, Jian Wang, and colleagues, National University of Singapore and the Medical School of Dalian University, China, have developed an organocatalytic inverse-electron-demand (IED) [3+2]cycloaddition reaction between a range of carbonyl compounds and diazoacetates. The reaction is catalyzed by secondary amines as a green promoter and proceeds efficiently at room temperature to generate substituted pyrazoles with high levels of regioselectivity.
The wide scope and ready availability of the starting materials, including ketones, β-ketoesters, β-diketones, and aldehydes, as well as the operational simplicity of this process, make this a convenient and practical method for the organocatalytic synthesis of pyrazoles.
- Highly Regioselective Organocatalyzed Synthesis of Pyrazoles from Diazoacetates and Carbonyl Compounds,
Lei Wang, Jiayao Huang, Xiaojie Gong, Jian Wang,
Chem. Eur. J. 2013.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201300047