The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) is one of the most important reactions in life processes such as respiration, and in energy conversion systems such as fuel cells. Slow ORR kinetics and the cost of commercial Pt-based catalysts have been major barriers against the commercialization of fuel cells.
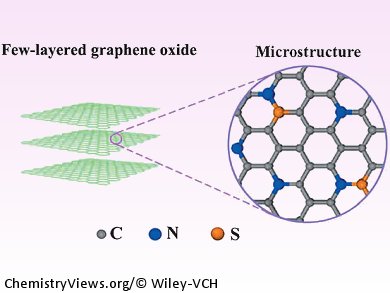
At the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Fuzhou, China, Lunhi Guan and co-workers have synthesized a carbon nanomaterial consisting of few-layered graphene oxide that has been dual-doped with S and N. The electrocatalyst has a N-dominant structure; however, the synergetic effect of the S and N co-doping reveals superior catalytic activity compared to mono N-doped, carbon-based catalysts. This new material also demonstrates improved overpotentials for metal-free, carbon-based ORR electrocatalysts.
In addition, Guan and his team have shown that S and N co-doped, few layered graphene oxide exhibits excellent stability and tolerance towards methanol, which is a major drawback of the Pt/C catalysts that are currently used commercially. Therefore, this new electrocatalyst demonstrates the potential to replace the current commercial cathodes, which could be key for the development of more commercially viable fuel cells.
- Sulfur and Nitrogen Co-Doped, Few-Layered Graphene Oxide as a Highly Efficient Electrocatalyst for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction,
Jiaoxing Xu, Guofa Dong, Chuanhong Jin, Meihua Huang, and Lunhi Guan,
ChemSusChem 2013.
DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201200564