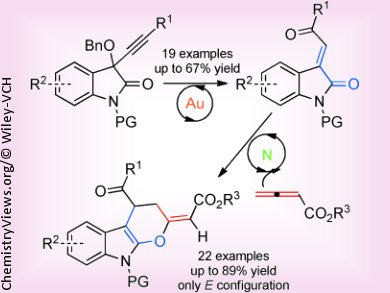
Polycyclic indoles represent interesting structural motifs for biologically active molecules in medicinal chemistry. However, the preparation often requires extensive synthetic efforts and multistep approaches. Di-Han Zhang and Min Shi, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, describe the usage of a binary catalytic system to achieve an efficient and highly regio- and stereoselective synthesis of polycyclic indoles starting out from isatin derivatives and allenic esters.
The sequential catalysis involves a gold-catalyzed rearrangement of a propargyl benzyl ether to the corresponding α,β-unsaturated ketone, and subsequently a [4+2] cycloaddition with an allenic ester to the desired polycyclic indole, catalyzed by a nitrogen-containing Lewis base. The synthesis requires very mild conditions, and a variety of substituents at different positions are tolerated, making this procedure an efficient entry to polycyclic indoles.
 Highly Stereoselective Synthesis of Polycyclic Indoles through Rearrangement/[4+2] Cycloaddition under Sequential Catalysis,
Highly Stereoselective Synthesis of Polycyclic Indoles through Rearrangement/[4+2] Cycloaddition under Sequential Catalysis,
Di-Han Zhang, Min Shi,
ChemistryOpen 2012, 1(5), 215–220.
DOI: 10.1002/open.201200028
ChemistryOpen – the first society-owned, open-access, chemistry journal – is a journal of ChemPubSoc Europe published by Wiley-VCH.