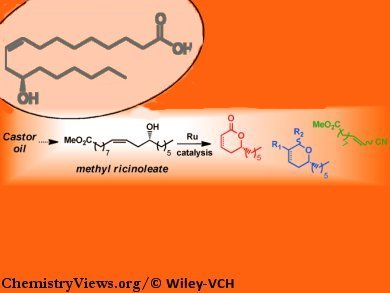
Cédric Fischmeister and Christian Bruneau, Université de Rennes, France, and colleagues show that methyl ricinoleate can be used as a platform chemical for the synthesis of a variety of functional compounds of interest both in fine chemistry and polymer synthesis. Ricinoleic acid (12-hydroxy-9-cis-octadecenoic acid) is an unsaturated omega-9 fatty acid. It naturally occurs in mature Castor plant seeds.
The modification of methyl ricinoleate by etherification of the hydroxyl group was accomplished by using a nonclassical ruthenium-catalyzed allylation reaction and also by esterification. Methyl ricinoleate derivatives were engaged in ring-closing metathesis (RCM) reactions leading to biosourced 3,6-dihydropyran and α,β-unsaturated lactone derivatives with concomitant production of polymer precursors. Sequential RCM/hydrogenation and RCM/cross-metathesis were also implemented as a straightforward method for the synthesis of tetrahydropyran and lactone derivatives as well as valuable monomers, i.e., polyamide precursors.
These first examples open up the route towards further utilization of methyl ricinoleate for the production of a broad range of functional molecules potentially accessible by the appropriate initial derivatization of the hydroxyl group preferentially using efficient and selective catalytic methods.
- Methyl Ricinoleate as Platform Chemical for Simultaneous Production of Fine Chemicals and Polymer Precursors,
Antoine Dupé, Mathieu Achard, Cédric Fischmeister, Christian Bruneau,
ChemSusChem 2012.
DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201200320