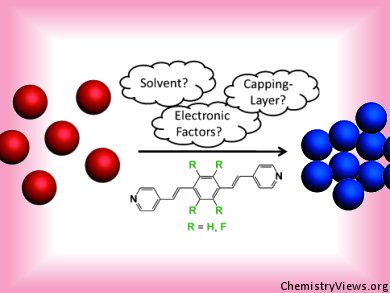
Researchers from the Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel, have made a systematic study to show that the aggregation and optical properties of gold nanoparticle assemblies are dependent on the nature of the organic cross-linkers and the compounds used to cap the gold nanoparticles.
Milko van der Boom and co-workers compared the formation of nanoparticle assemblies of citrate- and tetraoctylammonium bromide (TOAB) capped nanoparticles in water and in toluene, respectively. Two organic cross-linkers that comprise two vinylpyridine rings bridged by either an arene or fluorinated arene unit were used.
UV/Vis and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) studies showed that the citrate capped nanoparticles with the nonfluorinated cross-linker in water and the TOAB-capped nanoparticles with the fluorinated cross-linker in toluene underwent the highest degree of aggregation. Electronic factors, including the electronic structure of the cross-linker, and/or hydrophobic interactions are thought to play a role in the overall aggregation process.
Image: © Wiley-VCH
- Setting the Environmental Conditions for Controlling Gold Nanoparticle Assemblies,
Meital Orbach, Michal Lahav, Petr Milko, Sharon G. Wolf, Milko E. van der Boom,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201203291 - Meital Orbach, Michal Lahav, Petr Milko, Sharon G. Wolf, Milko E. van der Boom,
Angew. Chem. 2012.
DOI: 10.1002/ange.201203291


![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)