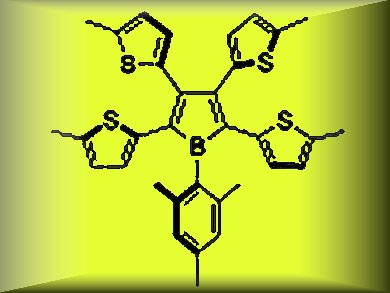
Borole is a boron-containing unsaturated five-membered ring with 4 π electrons. It is isoelectronic to a cyclopentadienyl cation (C5H5+). The most notable electronic feature of the borole skeleton in comparison to other heteroles is its significantly low-lying LUMO. Therefore, borole-based π-conjugated compounds have been widely recognized as electron-accepting systems.
Shigehiro Yamaguchi, Nagoya University, Japan, and colleagues report the synthesis of the tetrathienyl-substituted borole (3) (pictured) shown above as the first example of a heteroaryl-substituted borole. The combination of the electrondeficient and antiaromatic borole ring with the electron-donating aromatic thiophene rings produced a new type of borole-based π-conjugated system with an unusual electronic structure.
The incorporation of the electron-donating thienyl groups on the borole skeleton accentuates the electron-donating character of the borole ring, and leads to the narrow HOMO–LUMO gap and thus the characteristic absorption and electrochemical properties, which are significantly different from those of the known phenyl-substituted boroles.
These findings should provide an important guideline for the design of more fascinating boron-based π materials.
- Electron-Donating Tetrathienyl-Substituted Borole,
Takafumi Araki, Aiko Fukazawa, Shigehiro Yamaguchi,
Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5484–5487.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201201156