Coordination compounds with arylhydrazone ligands have been thoroughly investigated and are of great interest. They can have attractive biological applications, for example, as antimicrobial or anticancer agents. They can also have potential applications as magnetic materials due to their diverse architectures.
Amitabha Datta, Jadavpur University, Kolkata, India, and colleagues describe two distinct coordination compounds bearing aliphatic hydrazones as ligands and examine their biological effects in human colorectal carcinoma cells.
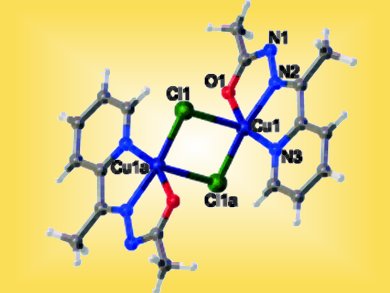
Single-crystal X-ray structural determination showed that the reaction of a tridentate hydrazone ligand with copper nitrate trihydrate in the presence of thiocyanate produced a 1D helical coordination chain. In the presence of copper chloride, a doubly chlorido-bridged dinuclear complex was found. Both bridging anions in the respective CuII complexes generate weak exchange-coupling interactions between the metal centers. Inhibitory effects on cell-population growth in human colorectal carcinoma cells were observed, particularly with the dinuclear complex (pictured).
Image: © Wiley-VCH
- End-to-End Thiocyanato-Bridged Helical Chain Polymer and Dichlorido-Bridged Copper(II) Complexes with a Hydrazone Ligand: Synthesis, Characterisation by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance and Variable-Temperature Magnetic Studies, and Inhibitory Effects on Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells,
K. Das, A. Datta, C. Sinha, J.-H. Huang, E. Garribba, C.-S. Hsiao, C.-L. Hsu,
ChemistryOpen 2012, 1(2), 80–89.
DOI: 10.1002/open.201100011
ChemistryOpen – the first society-owned, open-access, chemistry journal – is a journal of ChemPubSoc Europe published by Wiley-VCH.