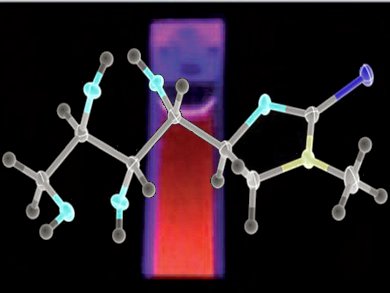
Water soluble quantum dots are amenable for bioconjugation, where the advantages include bright fluorescence and high photostability. Mark Green and colleagues, King’s College London, UK, have used a dithiocarbamate precursor to prepare water-soluble CdS quantum dots passivated with a nucleotide (see figure).

The isolation and identification by X-ray analysis of the decomposition product resulting from the water-soluble dithiocarbamate species used in the synthesis was also achieved. The identification of the decomposition product gives an understanding of the decomposition mechanism. This led the authors to suggest a new mechanism that compliments existing hypothesized decomposition routes for simple dithiocarbamates.
The material is bright and observable in the red region of the visible spectrum and perhaps useful in cell labeling.
Images: © Wiley-VCH
- Identifying the Decomposition Product of Single-Source Precursors: Towards Water-Soluble Quantum Dots,
M. Green, L. Sandiford, K. M. Anderson, Y. Ma,
ChemPlusChem 2012.
DOI: 10.1002/cplu.201100076
This article is available for free as part of the ChemPlusChem free trial.