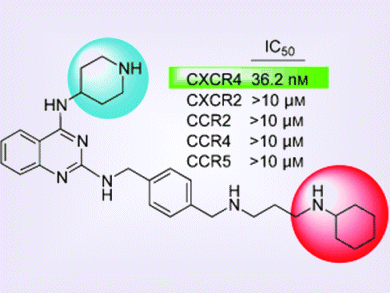
The CXCR4 chemokine receptor and its endogenous ligand CXCL12 play a pivotal role mobilizing many stem cell types. Compounds that block the CXCL12–CXCR4 interaction could be used in tissue repair and in the treatment of HIV, metastases, cancer, and inflammation.
A collaborative research effort led by Kak-Shan Shia, National Health Research Institutes, Taiwan, revealed a series of CXCR4 antagonists. Biological assays and animal efficacy studies show that these compounds are as potent as the current commercial drug AMD3100 (plerixafor, Mozobil™) in mobilizing hematopoietic stem cells to the peripheral circulatory system from bone marrow.
Because CXCR4 antagonists are able to mobilize adult stem cells without the need for surgery, they hold significant promise in cell therapy and regenerative medicine such as ischemic stroke recovery and heart tissue repair.
Image: © Wiley-VCH
- Discovery of Novel Stem Cell Mobilizers That Target the CXCR4 Receptor,
C.-H. Wu, C.-P. Chang, J.-S. Song, J.-J. Jan, M.-C. Chou et al.,
ChemMedChem 2012, 7 (2).
DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201100525