The family of 1,4:3,6-dianhydrohexitols, also known as isohexides, have proven to be excellent building blocks for the production of high performance biobased polymers such as polyamides and polyurethanes, owing to their intrinsic rigidity. The sugar based diols exist as three different stereoisomers: 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-d-glucidol (isosorbide), 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-dmannitol (isomannide), and 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-l-iditol (isoidide), derived from D-glucose, D-mannose, and L-fructose, respectively.
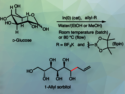
Daan S. van Es, Wageningen University & Research Centre, The Netherlands, developed a new, facile and scalable three-step route to obtain high purity dideoxy-diamino isohexides with absolute stereocontrol. The synthetic strategy encompasses three steps: transformation of the hydroxyl functionalities into efficient leaving groups, nucleophilic substitution with a protected amine, and catalytic removal of the protecting group, yielding the free amine.
The improved synthetic route is a valuable advance towards meeting scale and purity demands for evaluating the properties of new biobased performance materials, which will benefit the development of plastics.
- Renewable Rigid Diamines: Efficient, Stereospecific Synthesis of High Purity Isohexide Diamines,
S. Thiyagarajan, L. Gootjes, W. Vogelzang, J. van Haveren, M. Lutz, D. S. van Es,
ChemSusChem 2011.
DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201100398

![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)