The design and synthesis of IR/near-IR dyes has become an important topic in the area of solar cells, as the solar spectrum has a large photon flux in the region of 500–1000 nm. Improving the absorption of solar light in this region is one of the main ways of improving dye-sensitized solar cell (DSC) efficiencies.
Licheng Sun and co-workers, Dalian University of Technology, China, have made a dye for DSCs that gives the highest reported efficiencies of a donor-π spacer-acceptor (D-π-A ) organic dye in the near-IR region.
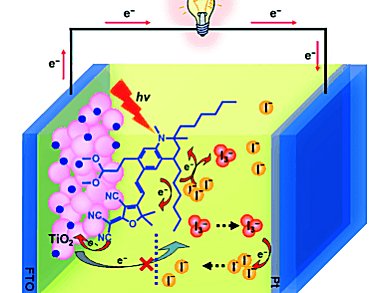
Long, flexible carbon chains in the lateral anchoring groups of the dye increase the power conversion efficiency dramatically. This performance enhancement can be ascribed to the prevention of the formation of molecular aggregates on the semiconductor nanoparticles, resulting in a lower recombination rate between transported electrons and I3− ions (pictured).
A cell based on the new dye, HY113, gives a maximum IPCE value of 93 % at 660 nm.
Image: © Wiley-VCH
- Molecular Design to Improve the Performance of Donor–π Acceptor Near-IR Organic Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Y. Hao, X. Yang, M. Zhou, J. Cong, X. Wang, A. Hagfeldt, L. Sun,
ChemSusChem 2011.
DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201100350