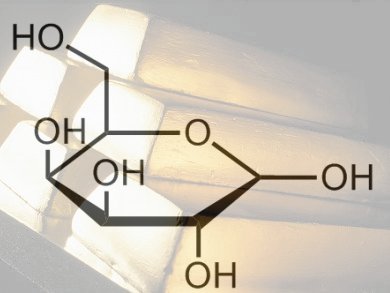
Woody biomass consists of lignocellulosic material, which is made up of three primary fractions: hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin. Extraction of hemicelluloses, and the rare and specialty sugars they contain such as ᴅ-galactose, can be easily achieved in water at moderate temperatures. This makes them prime candidates for sustainable feedstocks for fine chemicals.
To demonstrate how these sugars could be used as feedstocks, Dmitry Yu Murzin and co-workers, Åbo Akademi University, Finland, have studied the oxidation of ᴅ-galactose to galactonolactone then to galactonic acid (see scheme). They used molecular oxygen and Au nanoparticles supported on Al2O3 to oxidize ᴅ-galactose and investigated the influence of nanoparticle size and the pH values of the reaction medium.

Nanoparticles with a mean particle size of 2.6 nm exhibited the highest activity. Alkaline conditions gave high catalyst activity and selectivity to galactonic acid, while inhibition of the catalytic activity and poor selectivity were seen in the acidic medium.
- Selective Oxidation of ᴅ-Galactose over Gold Catalysts
B. T. Kusema, B. C. Campo, O. A. Simakova, A.-R. Leino, K. Kordás, P. Mäki-Arvela, T. Salmi, D. Y. Murzin,
ChemCatChem 2011.
DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201100183