The production of fine chemicals using continuous-flow methods is useful for green and sustainable chemistry. Catalytic reactions over packed-bed reactors reduce the formation of chemical wastes and avoid catalyst separation procedures. They can also enable direct connections of two or more reactions in sequence.
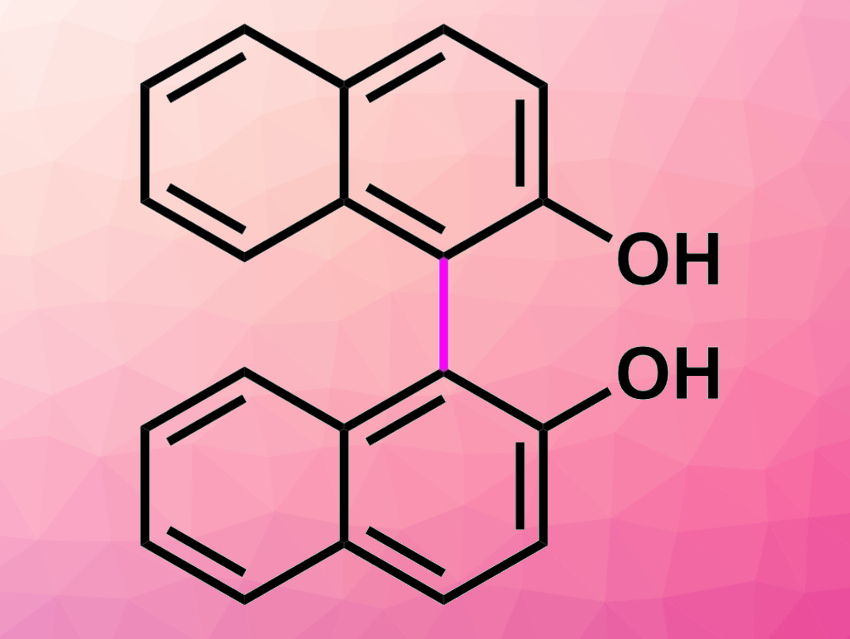
Shun-ya Onozawa, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Tsukuba, Japan, Shū Kobayashi, AIST and The University of Tokyo, Japan, and colleagues have developed an efficient continuous-flow synthetic method for biphenols and binaphthols using alumina-supported ruthenium hydroxide as a heterogeneous catalyst (pictured below). Oxygen was used as the sole oxidant for dehydrogenative coupling reactions of phenols and naphthols, yielding only water as a byproduct.

The team found that the Ru catalyst could be recycled at least three times by a simple online washing/activation procedure without depackaging the catalyst cartridge. They also showed that the approach can be used in a continuous-flow oxidation/hydrogenation sequence.
- Aerobic Dehydrogenative Coupling of Naphthols and Phenols with a Ru(OH)x/Al2O3 Catalyst under Continuous‐Flow Conditions,
Koichiro Masuda, Wenlong Chen, Kazushi Hayashi, Shigeru Shimada, Shun‐ya Onozawa, Nagatoshi Koumura, Kazuhiko Sato, Shū Kobayashi,
ChemistrySelect 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202102938